|
|
|
1.
|
|
(a)
|
For constant linear velocity,
the ratio of the distance x moved
to the time t, x/t = constant = v
or
x = vt.
|
(b)
|
For constant angular velocity,
the ratio of the angle Q
moved
to the time t, Q/t
= constant = w
or
Q= wt.
|
|
|
|
2.
|
|
(a)
|
Constant linear acceleration a
equals the change in linear velocity divided by the
time to change the velocity
a = (v - vo)/(t - 0)
or
v = vo + at.
|
(b)
|
Constant angular acceleration a
equals the change in angular velocity divided by the
time to change the velocity
a = (w
- wo)/(t - 0)
or
v = vo +
at.
|
|
|
|
3.
|
dx/dt
= v = vo + at, or dQ/dt
= w = wo +
at, or
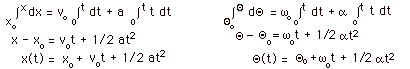
|
|
|
4.
|
(a) w(t)
= wo + at.
w(4.0 s) = p s-1
+ (4p s-2)(4.0
s) =17p s-1
|
(b)
|
Q(t)
= Qo
+ wot
+ 1/2 at2
|
| |
Q(4.0s)
= 0 + (p s-1)(4.0s)
+ 1/2 (4ps-2)(16s2)
|
| |
= 36p
|
In one rotation, the wheel turns through
an angle of 2p radians.
The number of turns made by the wheel = 36p/2p
= 18.
|
|
|
5.
|
(a) w(t)
= dQ/dt = d(b + ct + et2)/dt
= c + 2et. w(t1)
= c + 2et1
(b) a(t) = dw/dt
= d(c + 2et)/dt= 2e = constant = a(t1)
(c) v(t1) = w(t1)r
= (c + 2et1)r
(d) tangential acceleration, a(t1) = a(t1)r
= 2er
(e) centripetal or radial acceleration(t1) ={ v(t1)}2/r
= (c + 2et1)2r2/r
= (c + 2et1)2r
|
|
|
6.
|
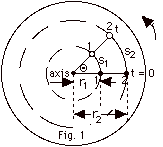
The constant angular velocity w
= (Q - 0)/(t - 0) = Q/t.
In time t, both points 1 and 2 rotate through angle Q
so both points have the same angular velocity. For point 1,
v1 = s1/t, and for point 2, v2
= s2/t. Since s2 > s1,
v2 > v1. This is also shown
from v1 = wr1
and v2 = wr2.
Again since r2 > r1, v2
> v1.
|
|
|
7.
|
Angular acceleration a
= (w10s -
wo)/(3 s - 0) =(6.0 rad/s - 0)/(3 s) = 2
rad/s2. Angle turned through from t = 0 to t =
10 s = wot + 1/2 at2
= 0 +
1/2(2 rad/s2)(100 s2) = 100 rad. w(10
s) = wo + at
= 0 + (2.0 rad/s2)(10s) =
20 rad/s. After t = 10 s, a
= 0. Angle turned through from t = 0 to t =
20 s Q (20 s) = Q10s
+ w10s +
1/2 at2 = 100
rad + 20 rad/s(10 s) + 0 = 300 rad.
|
|
|
|
|
9.
|
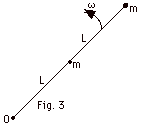
(a) I = mL2 + m(4L2) = 5mL2.
(b) In general, K = 1/2 Iw2.
For object closest to the axis O,
K
= 1/2 mL2w2.
For object farthest from O,
K
= 1/2 4mL2w2.
Total
K = 1/2 L2w2
(1 + 4) = 5/2(L2w2).
|
|
|
10.
|
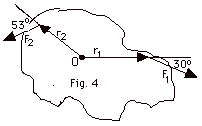
t
= r x F
t1
= r1F1 sin 300 = 2.0
m(1.5 N)(0.5) = 1.5 N-m
Point the fingers of your right hand in the direction of r1
and rotate it into F1 and your thumb points
into the page. t1
is into the page.
t2
= r2F2 sin 300 = 1.0
m(1.0 N)(0.8) = 0.5 N-m
Point the fingers of your right hand in the direction of r2
and rotate it into F2 and your thumb points
out of the page. t2
is out of the page. Resultant torque t
= (1.5 - 0.8)N-m = 0.7 N-m into the page.
|
|
|
11.
|
(a) Moment of inertia I of a rod about
one end is 1/3 mL2.
K = 1/2 Iw2
= 1/2(1/3mL2)w2.
(b) Let the initial position i be at the lowest position and
the final position f be at the highest position. Take the
gravitational potential energy of the center of the rod to
be zero at the lowest position, that is, Ui = 0.
The rod comes momentarily at rest at the highest position,
that is, Kf = 0. From conservation of energy, Uf
- Ui = (mg)change in height of center of
mass = Kf - Ki = 1/6 (mL2)w2.
Change in height of center of mass = (L2w2/6g).
|
|
|
12.
|

Assume the center of mass of the pencil
is at its center L/2 (Fig for # 12).
From conservation of energy,
|
Ui
|
+
|
Ki
|
=
|
Uf
|
+
|
Kf
|
|
mgL/2
|
+
|
0
|
=
|
0
|
+
|
1/2 Iw2
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
w
= (mgL/I)1/2 = (mgL/1/3 mL2)1/2
= (3g/L)1/2
|
|
vtop
of pencil = wL
= (3g/L)1/2L = (3gL)1/2
|
|
|
|
13.
|
|
(a)
|
See Fig. for #13 to the right,
|
 |
| |
tabout
pivot = Iabout pivot a
|
| |
L/2(Mg)sin 900
= 1/3 ML2 a
|
| |
a
= 3/2 (g/L)
|
(b) a = a
L = 3/2(g/L) (L) = 3g/2
|
|
|
|
|
15.
|
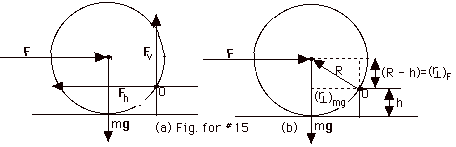
The forces on the wheel are shown in
Fig. for #15a above. Fh and Fv
are the horizontal and vertical forces, respectively, of the
curb on the wheel. These forces are not shown in Fig. for
#15b above because they do not produce a torque about axis
O. Figure for #15b shows the perpendicular distance to F
and mg from O. The perpendicular distance from
the axis O to the line of action of force F is (R -
h). The torque due to F = (R - h)F into the page.
The perpendicular distance from O to the line of action of
mg =
{R2 - (R - h)2}1/2 ={R2
- R2 + 2Rh - h2}1/2
= {2Rh - h2}1/2. The torque due
to mg = {2Rh - h2}1/2mg out of the page.
To rotate the wheel clockwise over the curb, the torque
into the page must be slightly larger than the torque out
of the page: (R - h)F > {2Rh - h2}1/2mg,
or F must be slightly greater than
{2Rh - h2}1/2mg/(R - h).
|
|
|
16.
|
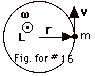
(a) L = r x mv. Because r x v is
out of the page (Fig. for #16), L is out of the page.
L = rmv sin  r,
v= rmv sin 900 = rmv. r,
v= rmv sin 900 = rmv.
(b) Since v = wr, L =
(mr2)w = Iw.
|
|
|
17.
|
| |
|
 |
|
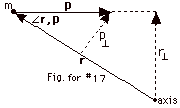
(a)
|
L = rp sin  r,
p = p(r sin r,
p = p(r sin  r, p) = pr
r, p) = pr
|
| |
|
|
(b)
|
L = r(p sin  r,
p) = r p r,
p) = r p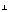
|
|
|
|
18.
|
| |
|
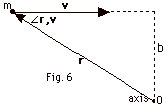 |
| |
L = r x mv
|
| |
L is into the page
|
| |
L = rmv sin  r r
|
| |
v = mv(r sin  r,
v) = mvb r,
v) = mvb
|
| |
|
|
|
|
19.
|
| |
|
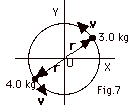 |
| |
L = r x mv
|
| |
L is out of the page for
both particles
(See Fig. 7 to the right)
|
| |
L = rmv sin  r r
|
| |
v = rmv sin 900
|
| |
Total L = 0.50 m(5.0 m/s)(3.0 +
4.0) kg
|
| |
=
17.5 kg-m2/s
|
| |
|
|
|
|
20.
|
| |
|
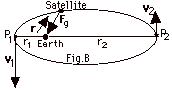 |
| |
t
= r x F
|
| |
t
=  r
F sin r, F r
F sin r, F
|
| |
|
For the satellite orbiting about the
earth as its axis,  r,
F = 1800. r,
F = 1800.
sin 1800 = 0 and the torque equals zero. When no
torque acts on a system, its angular momentum is conserved.
The angular momentum of the satellite at P1 = the
angular momentum of the satellite at P2.
|
|
|
21.
|
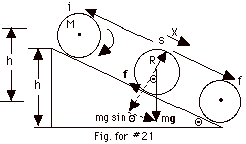
(a) The frictional force f acts at a point, not through
a distance so it does no work and energy is conserved. We
take the gravitational potential energy of the sphere equal
to 0 at the bottom of the hill, that is, Uf = 0.
The center of mass of the sphere at the top of the hill is
a distance h above where it is at the bottom of the hill:
Ui = Mgh. As the sphere rolls down the hill, it
has kinetic energy of translation of the center of mass and
it has rotational kinetic energy. From conservation of energy,
|
Ui + Ki
= Uf + Kf
|
|
Mgh + 0 = 0 + 1/2 Mv2
+ 1/2 Iw2 =
0 + 1/2 Mv2 + 1/2(2/5MR2)(v/R)2
|
|
Mgh = 7/10 Mv2 or v
= (10gh/7)1/2
|
(b)
|
(Fnet)x =
ma
|
|
|
Mg sin Q
- f = Ma
|
(Equation
1) |
Take the torques about the center of
mass. Since the weight passes through this axis, it produces
no torque.
|
t
= Ia
|
|
|
Rf sin 900 = (2/5 MR2)(a/R);
f = 2/5 Ma
|
(Equation
2) |
|
(i)
|
|
Substituting Eq. 2 into Eq. 1:
Mg sin Q - 2/5 Ma
= Ma or a = 5g sin Q/7
|
|
(ii)
|
|
From Eq. 2, f = 2/5 Ma = (2/5)M(5g
sin Q/7) = 2 Mg
sin Q/7
|
|
(iii)
|
|
v2 = vo2
+ 2as = 0 + 2(5g sin Q/7)s
= (10g/7)(s sin Q)
= (10g/7)(h)
|
v = (10gh/7)1/2 as found
in Part (a).
|
|
|
22.
|
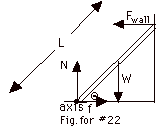
For equilibrium, S t =
0.
Taking the axis at the bottom of the ladder, with t
= r F sin  r,
F, r,
F,
S
t = L Fwall sin Q
- (L/2)W cos Q = 0
or
tan Q = W/(2
Fwall) (Equation
1)
Note that neither N nor f contributes to the torque when the
axis is at the bottom of the ladder because both forces pass
through the axis. Also for equilibrium,
|
S
Fx = 0
|
and
|
S
Fy = 0
|
|
f - Fwall = 0
f = Fwall
|
|
N - W = 0
|
| |
|
|
|
N
= W but f = µN
|
|
so f
= µW and µW = Fwall 51.30 (Equation
2)
|
Substituting Eq. 2 into Eq. 1:
|
tan Q
= W/2µW = 1/2µ = 1/0.80 = 1.25
|
|
Q
= 51.30
|
|
|
|
23.
|
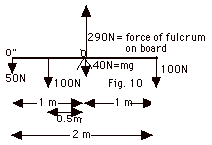
(a) Forces are shown in Fig. 10 above. The forces in addition
to those shown in the statement of the problem are the attraction
of the earth for the board = mg = 40 N and the force of the
fulcrum on the board. For equilibrium, the vector sum of the
forces = 0. 290 N - 50 N - 100 N - 40 N - 100
N = 0.
(b) Taking the axis at O, the net torque =
(1
m) 50 N + (0.5 m) 100 N - (1 m)100 N = 0
Neither the weight of the board nor the force of the fulcrum
on the board produce rotation about O because they pass through
the axis.
(c) About O", the sum of the torques =
-0.5
m(100 N) –1 m(40 N) – 2 m (100N) + 1 m(290 N)
-
50 N-m - 40 N-m - 200 N-m + 290 N-m = 0.
The force of 50 N at O" produces no torque. It does not
make any difference where you take the axis as long as you
stick with it through a single calculation.
|
|
|
24.
|
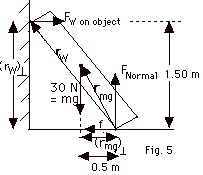
(a)
| |
S
Fy = 0
|
| |
Fnormal - mg = 0
|
| or |
Fnormal = mg = 30 N
|
(b) Take torques about the point where
the object touches the floor. Then neither the frictional
force nor the Fnormal contribute to the torque
because these forces pass through the axis. The perpendicular
component of the distance rW from the axis to the
point of application of FW is shown in Fig. 5 above
to be 1.50m. The perpendicular component of the distance
rmg from the axis to the point of application of
mg is shown in Fig. 5 to be 0.50m.
S t = 0 = +(0.5 m)30 N
- (1.50 m)(FW).
FW = 10 N.
(c) SFx
= 0 = FW - f or FW = 10 N = f
(d) µ = f/Fnormal = 10 N/30 N - 1/3
|
|