|
Outline - Magnetic Fields
|
|
- Magnetic Fields and Forces
- Forces on charged particles in a magnetic field B
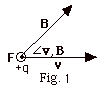
- Force F on a charge +q moving with a velocity
v in a magnetic field B is F = q(v
x B). F =qvB sin
 v,B.
The direction of F is given by pointing the
fingers of your right hand in the direction of v with
the palm of your hand toward B and then rotating
the palm of your hand into the direction of B.
The thumb of your right hand points in the direction of
the force. In Fig. 1 below, with the fingers of your right
hand in the direction of v when you rotate your
palm toward B, your thumb points out of the page
in the direction of F. A circle with a dot
in it, represents a vector out of the page. A circle
with an x in it, represents a vector into the page. F
is always perpendicular to v and B. F
is always perpendicular to the plane of v and B.
In Fig. 1, the plane of v and B is the plane
of the paper. v,B.
The direction of F is given by pointing the
fingers of your right hand in the direction of v with
the palm of your hand toward B and then rotating
the palm of your hand into the direction of B.
The thumb of your right hand points in the direction of
the force. In Fig. 1 below, with the fingers of your right
hand in the direction of v when you rotate your
palm toward B, your thumb points out of the page
in the direction of F. A circle with a dot
in it, represents a vector out of the page. A circle
with an x in it, represents a vector into the page. F
is always perpendicular to v and B. F
is always perpendicular to the plane of v and B.
In Fig. 1, the plane of v and B is the plane
of the paper.
- A negative charge moving to the right is the same as
a positive charge moving to the left. For a negative charge
moving to the right the magnetic force would be into the
page.
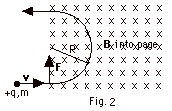
- For Fig. 2 above, a positively charged particle of charge
+q and mass m travelling with a velocity v to the
right enters a magnetic field B into the page.
The magnetic force F at the instant shown in the
figure is up perpendicular to v and to B.
Since there is no component of the force in the direction
of the velocity, there is no change in the magnitude of
the velocity, but there is a change in its direction.
The particle travels in a circle with uniform circular
motion.
Fnet
= ma
qvB sin 90o = mv2/R
qvB = mv2/R = 4p2mR/T2
= 4p2mRf2
since the period T = 2pR/v
= 1/f = 1/frequency.
- Forces on current-carrying wires in a magnetic field B
- Imagine a charge q moving with velocity v in a conductor
of length
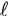 .
In time t, the charge moves .
In time t, the charge moves 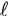 =
vt. Since v = =
vt. Since v = 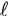 /t,
the magnetic force F = qvB sin /t,
the magnetic force F = qvB sin  v,
B = q( v,
B = q( 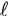 /t)B
sin /t)B
sin  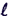 ,
B ,
B
=(q/t)( 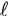 B) sin
B) sin  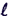 ,
B = I ,
B = I 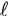 B
sin B
sin  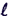 ,
B. F = I( ,
B. F = I(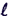 x
B). The direction of x
B). The direction of 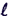 is
the same as the sense of the current I. is
the same as the sense of the current I.
- Point the fingers of your right hand in the direction
of
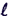 with
the palm of your hand toward B and then rotating
the palm of your hand into the direction of B.
The thumb of your right hand points in the direction of
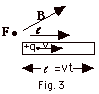
the force F. In Fig. 3 below, with the fingers
of your right hand in the direction of with
the palm of your hand toward B and then rotating
the palm of your hand into the direction of B.
The thumb of your right hand points in the direction of
the force F. In Fig. 3 below, with the fingers
of your right hand in the direction of 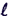 when
you rotate your palm toward B, your thumb points
out of the page in the direction of F. when
you rotate your palm toward B, your thumb points
out of the page in the direction of F.
- Practice Problems in 108
Problem Set for Magnetic Fields: 2 -
12.
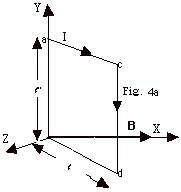
- Torque on a Current Carrying Loop in a Magnetic Field
 |
 |
- For Fig. 4a above, there will be equal forces up and down
on the upper and lower parts of the loop, respectively, but
they will not produce any torque about the Y-axis. The force
on length cd with current I,
 =
– =
–  j
and B = Bi is F = I(- j
and B = Bi is F = I(- 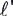 j x Bi) = I
j x Bi) = I 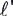 B k. The torque t
= (r x F), where r is drawn from the axis to
the point of application of the force F.
B k. The torque t
= (r x F), where r is drawn from the axis to
the point of application of the force F.
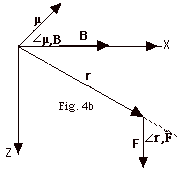
- It is easier to find the torque by looking at this in the
X-Z plane, as shown in Fig. 4b above. The angle between r
and F is
 r,F. r,F.
t = rF sin  r,F r,F
= 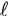 (I (I 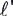 B)
sin B)
sin  r,F
= ( r,F
= (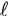 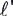 )B
sin )B
sin  r,F r,F
={(area of coil)I]B sin  r,F. r,F.
If there are N turns,
t={N(area of coil)I]B
sin  r,F
=µB sin r,F
=µB sin  µ,B µ,B
where µ= NI(Area) and the direction of µ
is found by curling the fingers of your right hand in the
direction of the current. Your thumb then points in the direction
of µ. Thus, t
= r x F = µx B. For the case
shown in Fig. 4b, t is
in the negative y or -j direction. In solving
problems, the quickest way to find the torque is with t
= µ x B.
- The magnetic energy of a dipole in a magnetic field B is
given by
- Practice Problems in 108
Problem Set for Magnetic Fields: 21,
32.
- Calculation of Magnetic Fields due to Current Distributions
- Magnetic Field due to a very long wire carrying current
I
- The magnitude of the field B = µoI/2pr,
where r is the perpendicular distance from the wire to
the point at which you wish to find the magnetic field.
µo = 4px
10-7 N/A2.
- Point the thumb of your right hand in the direction
of the current. The direction in which your fingers curl
is the direction of the magnetic field lines. For a very
long wire, the magnetic field lines are concentric circles
with the wire at the center of the circles.
- Look in the direction of the oncoming current in
Fig. 5a below. The magnetic field line is counterclockwise.
The magnetic field is tangent to the field line. Above
the wire, the field is out of the page. Below the
wire, the field is into the page.
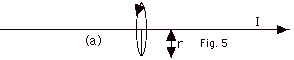
- It is easier to see this in Fig. 5b below. I have
rotated Fig. 5a through 90o and drawn
the current out of the page.
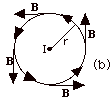
- The magnetic field due to a very long current-carrying
wire is to magnetism what the electric field due to a
point charge was to electricity. Know
B = µoI/2pr
and how to find the direction of B.
- Frequently you will be asked to find the magnetic field
due to two or more long current-carrying wires. Always
draw the magnetic field lines due to each wire in finding
the solution.
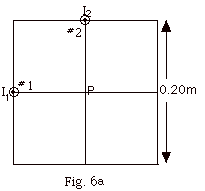
- In Fig. 6a below wire #1 carries a current I1
= 30 mA and wire #2 carries a current I2
=40 mA. Both currents are out of the page. Find the
resultant magnetic field B at point P at the
center of the square (Fig. 6a). The square has sides
= 20 cm.
- The magnetic field due to a long current wire =
µoI/2pr.
µo/2p
= 2 x 10-7 N/A2. For both
wires, r = 10 cm = 0.10 m.
B1 = 2 x 10-7 N/A2
(30 x 10-3 A/0.10 m)
= 60 x 10-9
N/A-m = 60nT.
B2 = 2 x 10-7 N/A2
(40 x 10-3 A/0.10 m)
= 80 x 10-9 N/A-m
= 80nT.
To find the direction of the magnetic fields due to
I1 and I2 at point P, draw the
magnetic field lines due to each wire such that they
pass through P. If you point the thumb of your
right hand in the direction of I1, you
find that the magnetic field line due to this current
is counterclockwise. At P (Fig.
6b below), the tangent to the curve (the perpendicular
to the radius) is up. Again from Fig. 6b, you
see the magnetic field line due to I2 is
counterclockwise and the tangent to the field line
at P is to the right. The resultant field at
P = B =(602 + 802)1/2 nT
= 100 nT. tan Q
= B1/B2 = 3/4. Q
= 37o.
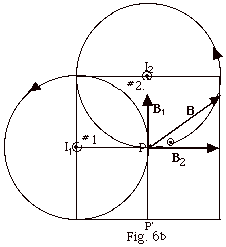
- Now show that if wire #2 is placed at P' in Fig.
6b above with the current into the page, you get the
same result as found in b. above.
- Practice Problems in 108
Problem Set for Magnetic Fields: 14-19.
- The Biot-Savart Law states
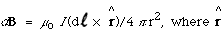
is a unit vector drawn from d 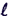 to P and d
to P and d 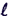 is in the direction of the current I.
is in the direction of the current I.
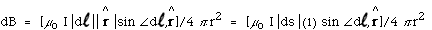
- Sample Problem
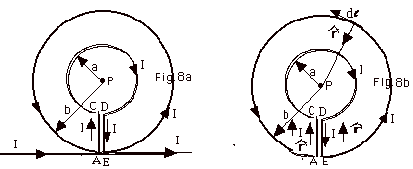
An otherwise infinite, straight, wire has two concentric
loops of radii a and b carrying equal currents in opposite
directions as shown in Fig. 8 below. Show that the magnitude
of the magnetic field at P, the common center of the loops,
is zero if a/b = p/(1
+ p). Try to
solve the problem before looking at the answer below.
The idea for this problem comes from Kenneth Ford, Classical
and Modern Physics (Zerox College Publishing).
- Solution to Sample Problem
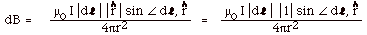
- A to C is 0o and sin 0o =
0.
There is no contribution from A to C.
- D to E is 180o and sin 180o =
0.
There is no contribution from D to E.
- C to D is 90o and sin 90o
= 1. From C to D,
dB = µoId 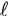 /4pa2 /4pa2
and since the length of the arc from C to D = 2pa,
the total field at P is
B = µoI(2pa)/4pa2
= µoI/2a.
Similarly, the field at P due to AE is µoI/2b.
The field due to the infinite wire is = µoI/2pb.
The field due to AE and the infinite wire is out of
the page and the field due to CD is into the page.
The field at P is zero if = µoI/2b
+ µoI/2pb
= µoI/2a or
if
1/b + 1/pb = (p+
1)/pb = 1/a or
a/b = p/(1
+ p).
- Practice Problems: 108
Problem Set for Magnetism: 28, 29
- Ampere's Law
Ampere's law states that the path integral of the magnetic
field around a closed path is equal to µo times
the current enclosed by the path.
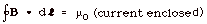
Use Ampere's law when B is constant everywhere along the path
and the  B,d B,d 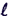 is
0, 90o, 180o, or 270o. is
0, 90o, 180o, or 270o.
- Application of Ampere's law to
- A very long current carrying wire gives B = µoI/2pr
- A very long solenoid gives B = µonI, where
I is the current
and n = the number of turns per unit length.
- A toroid of inner radius a and outer radius b gives for
- r < a, B = 0
- a < r < b, B = µoNI/2pr,
where N = the number of turns of the toroid.
- Practice Problems in 108
Problem Set for Magnetic Fields: 23-25, 28-30.
- Forces between two current-carrying wires
We wish to find the force of the long wire carrying current I1
on the long current-carrying wire with current I2
shown in Fig. 9a below.
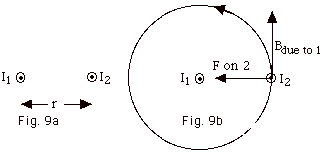
- The field due to I1 is Bdue to 1 =
µoI1/2p
r. With I1 out of the page, the magnetic
field line due to it is counterclockwise.
The force on 2 = I2  Bdue
to 1 sin Bdue
to 1 sin   ,
Bdue to 1. ,
Bdue to 1.
Since I2 is out of the page and Bdue to 1
is in the page of the paper, the angle is 90o.
The force per unit length on wire 2 = F on 2/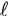 = I2Bdue to 1
= I2Bdue to 1
= I2(µoI1/2p
r). If you point the fingers of your right hand in the
direction of I2 and rotate your fingers into Bdue
to 1 your thumb points to the right in the direction
of the force on 2.
Now try to repeat the above finding the field due to 2 at
the position of wire #1. Then find the force on 1 due to Bdue
to 2, the magnetic field from the current in wire 2.
You will find the force on wire #1 is to the left. Newton's
third law is still in action. By experiment, we find
that two wires carrying current in the same direction attract
each other.
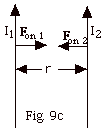
- It is more difficult, but not impossible, to visualize the
attraction between the two wires if they are drawn as shown
in Fig. 9c above. As you point your finger in the direction
of I1 and you look from above I1,
you see the magnetic field line is counterclockwise
and at the position of the second wire, the field is
into the page. Then with I2 up and Bdue
to 1 into the page, the force on 2 is to the right.
Now try it for the force on 1.
- Practice Problems in 108
Problem Set for Magnetic Fields: 13, 20, 23,
and 27.
|
|