|
|
|
1.
|
The same constant net force acts on
two different objects. A plot of velocity as a function of
time for the two objects is given in Fig. 1 below. The graph
labelled A is for object A; the one labelled B is for object
B. The mass of object A is 2.0 kg. Find (a) the acceleration
of object A, (b) the acceleration of object B, (c) the mass
of object B, and (d) the magnitude of the net force.
|
|
|
|
|
2.
|
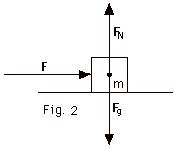
An object of mass m, resting on a horizontal
frictionless surface is acted upon by an applied force F,
the normal force of the surface FN and the
gravitational attraction of the earth Fg,
as shown in Fig. 2 below. Find Fg, FN
and the acceleration of the object when (a) F = 12 N and m
= 2.0 kg, (b) F = 24 N and m = 2.0 kg, (c) F = 12 N and m
= 1.0 kg. Take g = 10 m/s2.
|
|
 |
|
3.
|
In Fig. 2 above, the surface now exerts
a frictional force of 4.0 N on the object when it is in motion.
If the mass of the object m = 2 kg, find the acceleration
of the object when (a) F = 12 N and (b) F = 24 N.
|
|
|
4.
|
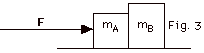
Two objects of mass mA =
2.0 kg and mB = 4.0 kg rest on a frictionless
surface (Fig. 3 below). An applied force F = 12 N acts on
object A, as shown in Fig. 3. Find (a) the acceleration of
the objects, (b) the force FAB of object B on A
and (c) the force FBA of object A on B.
|
|
|
|
5.
|
A rope is attached to a hook on a wall.
You pull on the rope, but it does not move. Discuss the forces
acting on the hook, the rope, and you. Which of these forces
are Newton third law of motion forces?
|
|
|
6.
|
The two objects in Fig. 3 above are now
connected by a massless string between A and B, string 1,
and pulled to the right by exerting a force of 12 N to the
right through another massless string, string 2, attached
to block B. Find (a) the acceleration of the blocks and (b)
the tension in string 1.
|
|
|
7.
|
(a) An object of mass m = 3.0 kg is set
into motion vertically and then raised with a constant velocity
of 3.0 m/s. What applied force F is needed? (b) The object
is now given an upward acceleration of 3.0 m/s2.
Now what applied force is needed? Take g = 10 m/s2.
|
|
|
8.
|
A system consisting of a rope of mass
0.10 kg between two blocks each of mass 0.10 kg is lifted
by an applied force F = 9.0 N (Fig. 4 below). (a) Find the
acceleration of the system. Find the tension at (b) the top
of the rope, and (c) the bottom of one-fifth of the rope.
Take g = 10 m/s2.
|
|
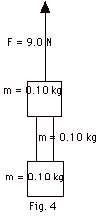
|
|
9.
|
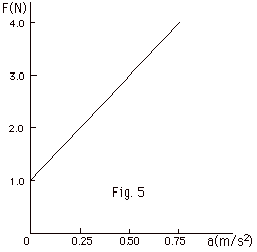
A block is pulled along a rough horizontal
surface. Figure 5 below is a plot of the applied force F as
a function of the acceleration of the block Find (a) the force
that must be applied to move the block with constant velocity,
(b) the mass of the block, (c) the force that must be applied
to give the block an acceleration of 1.0 m/s2.
(d) Suppose the experiment is repeated with a block of a greater
mass. If the new block is pulled along the same surface, how
will this change the graph? (e) Suppose the experiment is
repeated with the original block, changing only the surface
on which the block is pulled. How will this change the graph?
|
|
|
|
10.
|
A block of mass m = 2.0 kg is moved to
the right on a horizontal surface by a force of 26 N. The
coefficient of kinetic friction µk between
the surface and the object is 1/5. (a) Draw the object and
show all of the forces acting on it. Find (b) the frictional
force on the block and (c) the acceleration of the block.
Take g = 10 m/s2.
|
|
|
11.
|
Repeat problem 10 when the applied force
makes an angle of 22.6o above the horizontal.
|
|
|
12.
|
An object of mass m = 3.0 kg accelerates
down a frictionless inclined plane that makes an angle of
370 with the horizontal. (a) Show all the forces
acting on the object. Draw an X-axis parallel and down the
plane and a Y-axis perpendicular to the plane and upward.
(b) Find and draw the components of the forces on the X and
Y-axes. (c) Find the acceleration of the block. Take g = 10
m/s2.
|
|
|
13.
|
Repeat Problem 12 for a coefficient of
kinetic friction µk
between the surface and the object of 0.154.
|
|
|
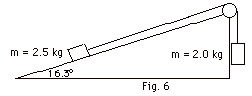
14.
|
The coefficient of kinetic friction between
the block of mass m = 2.5 kg and the plane in Fig. 6 below
is 1/6. Find (a) the acceleration of the block and (b) the
tension in the string. Take g = 10 m/s2.
|
|
|
|
15.
|
An object of mass m = 2 kg moves in a
circle on a table with uniform circular motion. The speed
of the object is 2 m/s and the radius of the circle is 0.5
m. Find the (a) frictional force acting on the object and
(b) total force of the table on the object.
|
|
|
16.
|
A man of mass 60 kg pushes on a sled
of mass 10 kg and the man and the sled accelerate forward
with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Neglect a frictional
force on the sled and find (a) the force of the man on the
sled, (b) the force of the sled on the man and (c) the frictional
force of the snow on the man.
|
|
|
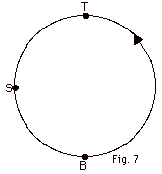
17.
|
A wooden rod of negligible mass is connected
to the shaft of a motor. An object with mass m = 2 kg is attached
to the other end of the rod. As the shaft rotates, the object
moves in a vertical circle of radius 0.5 m with a constant
speed of magnitude v = 3 m/s. (a) Find the magnitude of the
centripetal acceleration for this object. The vertical circle
path is shown in Fig. 7 below for an object that moves counter-clockwise.
Redraw the figure and show on it, the direction of the velocity
at (b) B, the bottom of the circle, (c) T, the top of the
circle and (d) S, the side of the circle. Now draw the direction
of the acceleration for (e) point B, (f) point T and (g) point
S Find the force of the rod on the object For
for (h) point B, (i) point T and (j) point S.
|
|
 |
|
18.
|
A 10-kg object rests on a scale in an
elevator. Find the reading on the scale when the elevator
moves with (a) a constant velocity of 5 m/s and (b) a constant
acceleration of 5 m/s2 upward. Take g = 10 m/s2.
|
|
|
19.
|
A person of mass m stands on a bathroom
scale in an elevator. Figure 8 below is a rough plot of scale
reading as a function of time. Describe the motion of the
elevator.
|
|
 |
|
20.
|
Two spheres of identical radii, one of
lead, the other of wood fall from rest in air from a certain
height. In this problem assume that the frictional force of
the air is the same on both spheres. Will the spheres reach
the ground at the same time?
|
|
|
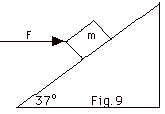
21.
|
A block with a mass m = 2.0 kg initially
at rest is pushed up the incline by a horizontal force F =
60 N (Fig. 9). The coefficient of kinetic friction between
the block and the incline µk =1/2. Find the
acceleration of the block.
|
|
 |