This
type of dilutions describes the ratio of the solute to the final volume of
the diluted solution.
For example, to make a 1:10 dilution
of a 1M NaCl solution, you would mix
one "part" of the 1M solution with nine "parts" of solvent (probably water),
for a total of ten "parts." Therefore,
1:10 dilution means 1
part + 9 parts of water (or other diluent).
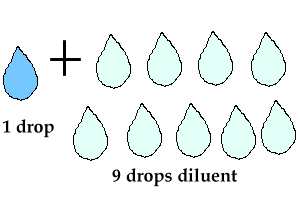
For example: if you needed 10
mL of the 1:10 dilution, then
you would mix 1mL of the 1M NaCl
with 9mL of water.
Or: if you needed 100mL of the
1:10 dilution, then you would
mix 10mL of the 1M NaCl with
90mL of water.
The final concentration of NaCl
in both cases is 0.1M.